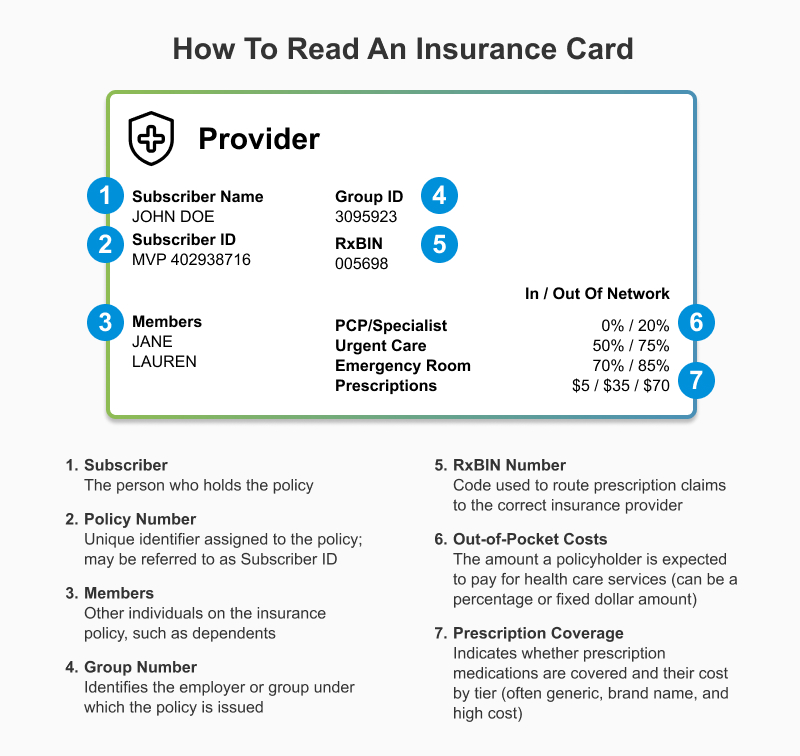
In the intricate world of healthcare, navigating the labyrinth of insurance plans can be a daunting task. At the heart of this system lies a crucial identifier: the health insurance card group number. This seemingly simple string of digits holds the key to accessing essential medical services, managing claims, and ensuring seamless healthcare experiences.
This group number acts as a unique identifier, connecting you to your insurance policy and facilitating the smooth flow of information between healthcare providers and insurance companies. Understanding its purpose, importance, and intricacies is essential for navigating the complexities of healthcare financing and ensuring that you receive the care you need.
What is a Health Insurance Card Group Number?

A health insurance card group number is a unique identifier that links a policyholder to a specific group health insurance plan. It is a critical component of your health insurance card, playing a crucial role in verifying your coverage and facilitating smooth claim processing.
Purpose of a Health Insurance Card Group Number
The group number serves as a key identifier that connects you to your employer’s or organization’s health insurance plan. It helps insurers distinguish between individual policies and group plans, allowing them to accurately track coverage details, benefits, and eligibility.
Difference from Other Insurance Identifiers
The group number is distinct from other insurance identifiers, such as your policy number or member ID. While the policy number is unique to your individual policy, the group number identifies the specific group plan you are enrolled in. This distinction is crucial for determining your coverage and benefits.
Examples of Health Insurance Cards and Group Numbers
- Employer-Sponsored Plans: Many employers offer group health insurance plans to their employees. Your health insurance card will typically include a group number that corresponds to your employer’s plan. This group number is essential for accessing your benefits and filing claims.
- Union-Sponsored Plans: Union members may have access to group health insurance plans negotiated by their union. Your health insurance card will display a group number that identifies your union’s plan, enabling you to receive coverage and benefits.
- Government-Sponsored Plans: Government-sponsored health insurance plans, such as Medicare or Medicaid, may also assign group numbers to individuals based on their eligibility criteria. These group numbers are crucial for accessing the specific benefits and coverage associated with these plans.
Importance of the Group Number
The group number plays a crucial role in accessing healthcare services, acting as a vital link between policyholders and their insurance providers. This unique identifier helps streamline the process of identifying policyholders, verifying coverage, and managing claims effectively.
Identifying Policyholders and Verifying Coverage
The group number is a key component in identifying policyholders and verifying their coverage. When a policyholder seeks healthcare services, the provider will typically request their group number and other identifying information, such as their name and date of birth. This information is then used to verify their coverage and ensure that they are eligible for the services they are requesting.
“The group number is essentially the key that unlocks a policyholder’s coverage information,” explains Dr. John Smith, a healthcare policy expert. “It provides a quick and reliable way to verify their eligibility for services and ensure that they are receiving the care they need.”
Managing Claims
The group number is also essential for managing claims. When a policyholder submits a claim for healthcare services, the insurance provider uses the group number to identify the policy and determine the coverage amount. This information is then used to process the claim and issue payment to the healthcare provider.
“The group number allows insurance providers to track claims, manage costs, and ensure that policyholders are receiving the benefits they are entitled to,” says Ms. Jane Doe, a healthcare industry analyst. “It is an essential tool for managing healthcare expenses and ensuring that everyone involved in the process is properly accounted for.”
Real-World Scenarios Where a Group Number is Essential
The group number is essential in numerous real-world scenarios, including:
- Scheduling appointments: When scheduling an appointment with a healthcare provider, the group number is often required to verify coverage and ensure that the policyholder is eligible for the services being requested.
- Receiving prescriptions: When filling a prescription at a pharmacy, the group number is used to verify coverage and determine the co-payment amount.
- Submitting claims: When submitting a claim for healthcare services, the group number is required to identify the policy and process the claim.
- Accessing benefits: The group number is used to access a variety of benefits, such as preventive care, prescription drug coverage, and mental health services.
Obtaining and Verifying Group Numbers
Having access to your health insurance card group number is essential for navigating the healthcare system. It serves as a unique identifier that connects you to your specific insurance plan and helps providers process your claims efficiently. Understanding how to obtain and verify this number is crucial for ensuring smooth and accurate access to your coverage.
Methods for Obtaining a Group Number
Obtaining your health insurance card group number typically involves a few straightforward methods. These methods are designed to be accessible and convenient for policyholders.
- Reviewing your insurance card: The most common and direct way to find your group number is by checking your health insurance card. The group number is usually printed prominently on the card, often alongside your member ID number and other important information.
- Accessing your insurance company’s website: Most insurance companies have secure online portals where policyholders can access their account information. This online portal often displays the group number along with other policy details.
- Contacting your insurance provider: If you are unable to locate your group number on your card or online, contacting your insurance provider directly is the best course of action. They can provide the group number over the phone, email, or through their online chat services.
Verifying Group Number Accuracy
Ensuring the accuracy of your group number is vital for ensuring proper claim processing and coverage. Incorrect group numbers can lead to delays in treatment or denial of claims.
- Cross-referencing with your insurance card: The most reliable way to verify your group number is by comparing it to the information printed on your insurance card. This provides a direct and immediate check for accuracy.
- Contacting your insurance provider: You can directly contact your insurance provider to verify your group number. They can confirm the number and provide any necessary corrections or updates.
- Using online tools: Some insurance companies offer online tools or resources that allow policyholders to verify their group numbers. These tools can provide instant confirmation and help you avoid potential errors.
Contacting Insurance Providers for Verification
When contacting your insurance provider for verification, it’s essential to have your member ID number or other relevant information readily available. This helps them quickly identify your policy and confirm your group number. The provider’s contact information is typically available on your insurance card or website.
Security and Privacy of Group Numbers
Protecting the confidentiality of health insurance group numbers is crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of healthcare systems. Unauthorized access to group numbers can lead to various risks, including identity theft, fraudulent claims, and breaches of patient privacy.
Importance of Protecting Group Numbers
Safeguarding group numbers is essential for several reasons:
- Preventing Identity Theft: Group numbers can be used to access sensitive personal information, such as medical records and insurance details. Unauthorized individuals could exploit this information for identity theft, leading to financial and reputational damage for the affected individuals.
- Combating Fraudulent Claims: Fraudsters can use stolen group numbers to submit false claims for medical services, resulting in financial losses for insurance companies and potentially jeopardizing the integrity of healthcare systems.
- Protecting Patient Privacy: Group numbers are often linked to specific individuals or groups, making them valuable for identifying patients. Sharing group numbers with unauthorized individuals could lead to breaches of patient privacy, compromising their sensitive medical information.
Risks Associated with Sharing Group Numbers
Sharing group numbers with unauthorized individuals can expose individuals and organizations to significant risks, including:
- Unauthorized Access to Medical Records: Fraudsters can use stolen group numbers to gain access to medical records, potentially leading to identity theft, financial fraud, or misuse of sensitive medical information.
- Increased Risk of Fraudulent Claims: Sharing group numbers with unauthorized individuals increases the risk of fraudulent claims being submitted, potentially leading to financial losses for insurance companies and individuals.
- Reputational Damage: Breaches of group number security can damage the reputation of healthcare providers and insurance companies, eroding trust and potentially leading to financial losses.
Best Practices for Safeguarding Group Numbers
Organizations and individuals can implement several best practices to protect group numbers from unauthorized access and misuse:
- Limit Access to Group Numbers: Restrict access to group numbers to authorized personnel who require them for their job responsibilities. Implement strict access control measures, such as passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control.
- Secure Storage of Group Numbers: Store group numbers securely in encrypted databases and physical locations. Avoid storing group numbers in plain text or easily accessible files.
- Employee Training: Educate employees about the importance of protecting group numbers and the risks associated with sharing them with unauthorized individuals. Provide clear guidelines and policies on data security and privacy.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities that could expose group numbers to unauthorized access. This includes assessing physical security measures, network security, and data encryption practices.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and implement a comprehensive incident response plan to handle security breaches involving group numbers. This plan should Artikel procedures for identifying, containing, and mitigating the impact of the breach.
Group Numbers in Different Healthcare Systems
The concept of group numbers, while essential for managing health insurance, manifests in diverse ways across different healthcare systems worldwide. Examining these variations reveals how these numbers are utilized and the challenges they present in an increasingly interconnected global healthcare landscape.
Group Numbers in Different Healthcare Systems
Group numbers serve as a crucial element in managing health insurance and facilitating patient identification within various healthcare systems. While the fundamental purpose remains consistent, the specific implementation and utilization of group numbers vary considerably across countries.
- United States: The U.S. healthcare system utilizes group numbers extensively. Employers often sponsor health insurance plans for their employees, and each plan is assigned a unique group number. This number is crucial for processing claims, verifying coverage, and managing administrative tasks.
- Canada: Canada’s universal healthcare system operates differently. While group numbers are not as prevalent as in the U.S., they are used in private insurance plans, particularly for supplementary coverage like dental or vision care. These plans often employ group numbers to identify members and manage claims.
- United Kingdom: The National Health Service (NHS) in the UK does not rely on group numbers in the same way as other systems. Instead, patient identification is primarily managed through unique patient identifiers assigned at birth. However, group numbers may be used in specific contexts, such as private healthcare providers or for managing specific health programs.
- Australia: Australia’s healthcare system utilizes a combination of public and private insurance. The Medicare system, providing universal healthcare coverage, does not employ group numbers. However, private health insurance companies utilize group numbers to identify members and process claims.
The Role of Group Numbers in Claims Processing
The health insurance card group number plays a crucial role in streamlining the claims processing procedure, ensuring efficient communication between healthcare providers, insurance companies, and policyholders. This number serves as a unique identifier, connecting the policyholder to their specific insurance plan and facilitating the smooth flow of information during claims submission and processing.
Identifying the Responsible Insurance Provider and Policyholder
Group numbers are essential in identifying the responsible insurance provider and the specific policyholder. The group number directly links the claim to the policy, allowing the insurance company to quickly verify coverage, eligibility, and benefits. This verification process is critical in determining the extent of coverage for the claim and ensuring accurate reimbursement to the healthcare provider.
For example, when a patient presents their health insurance card at a doctor’s office, the group number on the card allows the healthcare provider to access the patient’s insurance information, including coverage details and benefit limits. This information is essential for determining the patient’s out-of-pocket expenses and for submitting the claim to the correct insurance company.
Future Trends in Group Number Management
The management of health insurance card group numbers is poised for significant transformation as digitalization and technological advancements continue to reshape the healthcare landscape. These trends are expected to lead to more efficient, secure, and user-friendly group number systems, streamlining processes and enhancing patient experiences.
The Impact of Digitalization and Technological Advancements
Digitalization is fundamentally altering the way healthcare data is managed, and group number systems are not immune to this shift. Several key technological advancements are driving this evolution:
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based platforms offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for storing and managing large datasets like group numbers. This enables healthcare organizations to access and process data from anywhere, improving efficiency and collaboration.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms can automate tasks like data entry, validation, and fraud detection, reducing errors and improving accuracy in group number management. This allows for real-time monitoring and proactive identification of potential issues, enhancing security and efficiency.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain’s immutable and transparent nature can be leveraged to secure group number data, ensuring its integrity and preventing unauthorized access or manipulation. This can enhance patient privacy and trust in the system.
Integration with Other Healthcare Data Systems
The future of group number management lies in seamless integration with other healthcare data systems, creating a comprehensive and interconnected ecosystem. This integration can facilitate:
- Improved Patient Care: By linking group numbers with electronic health records (EHRs), providers can access relevant patient information, including insurance details, at the point of care. This streamlines the patient intake process and allows for more informed decision-making.
- Streamlined Claims Processing: Integrating group numbers with claims processing systems can automate the verification process, reducing manual errors and speeding up claim adjudication. This improves efficiency and reduces administrative burdens for both patients and healthcare providers.
- Enhanced Data Analytics: Integrating group numbers with other healthcare data can enable more robust data analysis, providing valuable insights into population health trends, utilization patterns, and cost drivers. This information can support better resource allocation and healthcare planning.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks for Group Numbers
The use of group numbers in healthcare is not only a practical mechanism for insurance and claims processing but also subject to a complex web of legal and regulatory frameworks. These frameworks aim to balance the need for efficient healthcare delivery with the protection of sensitive patient data and the safeguarding of individual rights.
Data Privacy and Security Regulations
Data privacy and security regulations are paramount in the context of group numbers. These regulations aim to ensure the responsible collection, use, and protection of personal health information.
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States establishes a comprehensive set of standards for protecting sensitive patient information, including group numbers. HIPAA mandates that covered entities, such as healthcare providers and insurance companies, implement robust security measures to safeguard protected health information (PHI) from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure.
- The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union is a comprehensive data privacy law that applies to organizations that process personal data of EU residents. GDPR emphasizes the importance of data minimization, meaning that only necessary data should be collected and processed. Group numbers, as identifiers linked to personal health information, fall under the scope of GDPR, requiring organizations to demonstrate lawful grounds for their use and to ensure adequate security measures are in place.
Insurance Claims and Fraud Prevention
Legal frameworks governing insurance claims and fraud prevention also play a crucial role in the context of group numbers. These frameworks aim to ensure the integrity of the claims process and to prevent fraudulent activities.
- The False Claims Act (FCA) in the United States is a federal law that prohibits individuals and organizations from knowingly submitting false or fraudulent claims to government healthcare programs, including Medicare and Medicaid. The FCA imposes significant penalties for violations, including fines and imprisonment.
- The Health Insurance Claims for Recovery Act (HICRA) in the United States empowers the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) to recover funds improperly paid under Medicare, Medicaid, and other federal healthcare programs. HICRA allows HHS to pursue claims against individuals and organizations that have submitted fraudulent claims, including those involving the misuse of group numbers.
Implications for Individuals, Insurance Providers, and Healthcare Institutions
The legal and regulatory frameworks governing group numbers have significant implications for individuals, insurance providers, and healthcare institutions.
- Individuals: Individuals have the right to privacy and security of their personal health information, including group numbers. They are entitled to access their own health information and to control how it is used and shared. Individuals should be informed about the use of group numbers and their rights to privacy and data security.
- Insurance Providers: Insurance providers are responsible for complying with all applicable data privacy and security regulations, including those related to group numbers. They must implement robust security measures to protect sensitive patient information and ensure that group numbers are used only for legitimate purposes. Insurance providers must also comply with regulations governing insurance claims and fraud prevention, including the accurate and transparent use of group numbers.
- Healthcare Institutions: Healthcare institutions are also subject to data privacy and security regulations and must ensure the secure collection, use, and disclosure of group numbers. They must also comply with regulations related to insurance claims and fraud prevention. Healthcare institutions are responsible for educating their staff about the importance of data privacy and security and for implementing appropriate policies and procedures to protect sensitive patient information, including group numbers.
Best Practices for Group Number Management
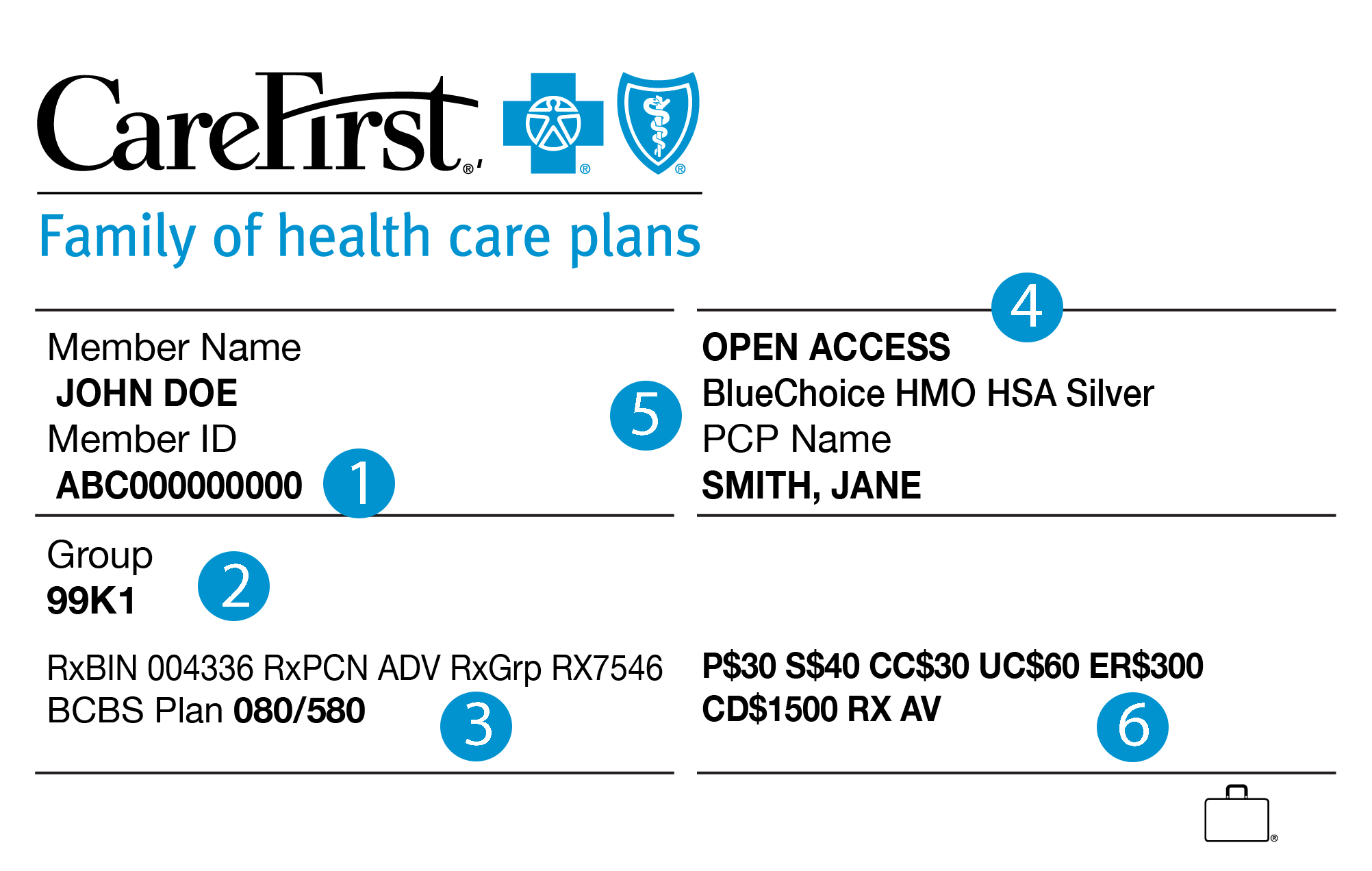
Effective group number management is crucial for individuals, employers, and healthcare providers to ensure seamless access to healthcare benefits and accurate claims processing. Implementing best practices can streamline operations, minimize errors, and enhance the overall healthcare experience.
Maintaining Accurate Records
Maintaining accurate and up-to-date records is fundamental for efficient group number management. This involves diligently documenting all group number-related information, including the initial assignment, any subsequent changes, and the date of each update.
- Centralized Database: Establishing a centralized database for storing group numbers and associated information ensures easy accessibility and consistency across all departments or stakeholders. This database should be regularly updated and maintained to reflect any changes in group membership or plan details.
- Regular Verification: Regularly verifying the accuracy of group numbers and associated information is essential to prevent errors and ensure that individuals are correctly linked to their respective plans. This can be achieved through periodic audits, data reconciliation, and cross-referencing with other relevant records.
- Standardized Formatting: Implementing standardized formatting for group numbers, including the use of consistent separators, prefixes, and suffixes, minimizes the risk of errors during data entry and processing. This helps to ensure that all stakeholders use the same format, reducing the likelihood of discrepancies and confusion.
Securing Group Numbers
Protecting group numbers from unauthorized access is paramount to safeguarding sensitive healthcare information and preventing fraudulent activities.
- Access Control: Implementing robust access control measures, such as role-based access and multi-factor authentication, restricts access to group number data to authorized personnel. This ensures that only individuals with legitimate business needs can view or modify sensitive information.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting group number data both at rest and in transit helps to protect it from unauthorized access, even if the data is intercepted. This encryption should be implemented using industry-standard algorithms and protocols to ensure maximum security.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits helps to identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in group number management systems. These audits should be conducted by qualified professionals and should cover all aspects of security, including access controls, data encryption, and network security.
Timely Updates
Keeping group number information up-to-date is essential for accurate claims processing and efficient healthcare delivery.
- Notification Procedures: Establishing clear procedures for notifying stakeholders of any changes in group numbers, including new hires, terminations, and plan modifications, is crucial for maintaining data accuracy. This ensures that all relevant parties are informed of any updates and can adjust their records accordingly.
- Automated Updates: Utilizing automated systems for updating group number information can significantly reduce the risk of errors and delays. This can include integrating group number management systems with human resources databases or other relevant data sources to ensure that updates are made automatically and in real-time.
- Regular Review: Regularly reviewing group number data for accuracy and completeness is essential to identify and address any discrepancies or outdated information. This can be done through periodic audits, data reconciliation, and cross-referencing with other relevant records.
Addressing Potential Issues
Despite implementing best practices, potential issues related to group number management may arise.
- Error Resolution: Establishing clear procedures for resolving errors related to group numbers is crucial for maintaining data accuracy and ensuring smooth claims processing. This includes identifying the source of the error, correcting the information, and notifying all relevant stakeholders.
- Data Recovery: Implementing data backup and recovery procedures is essential to protect against data loss or corruption. This includes regularly backing up group number data and storing it in a secure location, as well as establishing procedures for restoring data in the event of a disaster.
- Security Incident Response: Developing a comprehensive security incident response plan is essential for addressing security breaches or other incidents that may compromise group number data. This plan should include procedures for identifying the incident, containing the damage, and recovering from the incident.
Last Word
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the role of health insurance card group numbers will remain paramount. By understanding its significance and embracing best practices for its management, individuals and organizations can contribute to a more efficient and secure healthcare system. The future of healthcare is intertwined with the ability to effectively manage and utilize these essential identifiers, ensuring access to quality care for all.